Induction
Cooking
Unlike gas cooktops in which the energy is converted to heat then directed to the pan or pot, induction cooking directly supplies the energy to the cooking vessel through
the magnetic field, minimizing heat loss. To achieve the same level of power output, induction cookers require much less power input than its gas counterparts,
hence cutting energy cost by up to 65%.

Induction
Cooking

Traditional
Gas Cooking
High Energy Efficiency
High Heating Speed
Accurate Temperature
| Induction Cooking | Traditional Gas Cooking | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency |
Allows most of the heat generated to be used for heating, hence very little heat loss and high energy efficiency.
|
Much higher heat loss as some energy is used to heat up the surrounding air. When using a gas cooker, more energy input is required to achieve the same level of heat produced by an induction cooker.
|
| Heating Speed |
Energy is converted to heat and then directed to the cookware. Energy is supplied directly to the cooking vessel through the magnetic fi eld. 80% of the energy from the electricity is used for cooking.
|
Less than 45% of energy is used for cooking.
|
| Precise Temperature Control |
Combined with advanced temperature precision control,actively detects the temperature of the cookware. Once the temperature reaches the desired level (set by theuser), the heating process
stops.
|
No automatic temperature control function. Heating
of the cookware continues unless the user manually
lowers thepower.
|
| Less Fumes |
No open flame and produces less fumes.
|
Heat source comes from different flammable gases
such as natural gas, butane, propane or liquefi ed
petroleum gas and generates fumes.
|
| Comfortable Kitchen Temperature |
Heat is generated from within the cookware so very little energy is wasted into the kitchen’s atmosphere, which makes the working environment more comfortable.
|
Heat is generated from the hob surface. The surrounding air is also heated and the kitchen tempe rature becomes higher.
|
| Safety |
No open flame or heated surface to catch fire or getburns.
|
With open flame and higher chances of fi re and burns.
|
| Economic |
Uses energy efficiently and signifi cantly cuts down energy bills.
|
A large sum of the energy is not used directly for heating the food but dissipated during the process, hence higher energy bills.
|
Separation of the Heating Coil and the Boiling Oil / Water, V-type Tank Design -
Even Heat Distribution, Durable and Lengthened Frying Oil Life
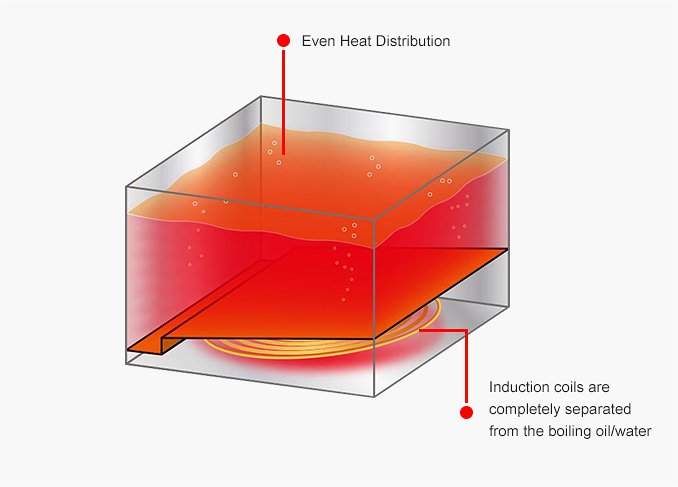
induction fryers and noodle cookers / fryers use induction coils that are completely separated from the boiling oil/water. This makes the equipment more durable and safe while lengthening the life of frying oil. Also, heat is transferred from the bottom to the top evenly, covering the whole tank, delivering consistent and tasty results.
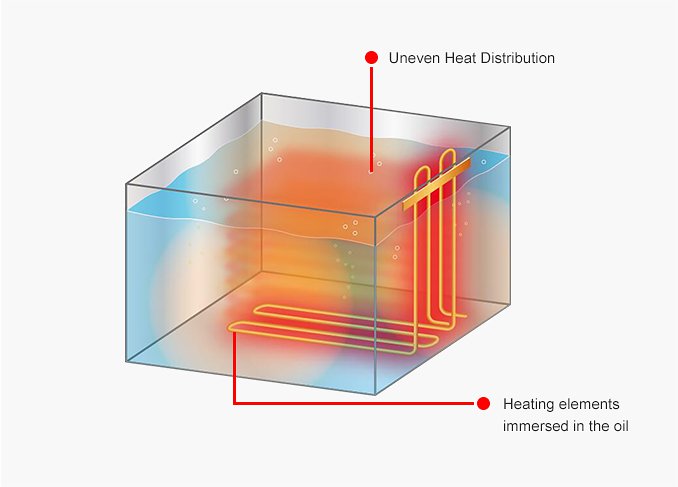
Both electric fryers and electric noodle boilers use heating elements mmersed in the oil, which leads to uneven heat distribution and quick wearing out of the heating elements. At the same time, the frying oil used darkens quickly and needs frequent replacement.
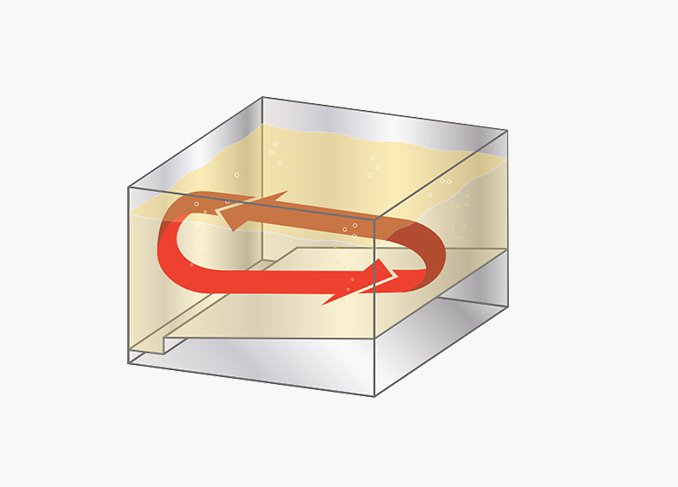
V-type tank design with special oil guiding board causes oil to flip, avoiding sticking of foods while expanding oil life.
| Induction Steamer&Fryer | Electric Steamer&Fryer (Direct Immerse heating element) |
|
|---|---|---|
| (η) Efficiency (η) | 80% | 65% |
| Temperature Control | Yes (Average Power Requirements 70%) |
No |
| (Pin) Power Input (Pin) | (η) Efficiency (η) | (η) Efficiency (η) |
| (Pin) Power output (Pin) | (η) Efficiency (η) | (η) Efficiency (η) |
| For the same Power Output | ||
| Power Input | 1.25 * (Power Output * 0.7) (w/ TemperatureControl) |
1.05 * Power output (w/o Temperature control) |
| Energy requirements | 1 : 1.2 | |
| Energy Savings | Save 17% (1.2-1) / 1.2 |
| Induction Cooking | Traditional Elcetric Cooking | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency |
Allows most of the heat generated to be used for heating,hence very little heat loss and high energy efficiency.
|
Much higher heat loss as some energy is used to heat up the surrounding air. More electricity is required to achieve the same level of heat produced by an induction cooker.
|
| Heating Speed |
Energy is converted to heat and then directed to the cookware. Energy is supplied directly to the cooking vessel through the magnetic field. 80% of the energy from the electricity is used for cooking.
|
Less than 50% of energy is used for cooking.
|
| Precise Temperature Control |
Combined with advanced temperature precision control,actively detects the temperature of the cookware. Once the temperature reaches the desired level (set by theuser), the heating process stops.
|
No inverter feature. Heating of the cookware continues unless the user manually lowers the power.
|
| Less Fumes |
Only the cookware is heated, producing less fumes.
|
Relies on the heating elements. When heating is in progress more fumes are generated.
|
| Comfortable Kitchen Temperature |
Heat is generated from within the cookware so very little energy is wasted into the kitchen’s atmosphere, which makes the working environment more comfortable.
|
Heat is generated from the hob surface. The surrounding air is also heated and the kitchen temperature becomeshigher.
|
| Safety |
The cooker itself does not bear much heat compared with electric cookers, hence much lower chances of fi re or burns.
|
Heating coil will heat up fi rst before transferring the energy to the cookware. The cooker itself gets hot and poses higher risks of fire or burns.
|
| Economic |
Uses energy effi ciently and signifi cantly cuts down energy bills.
|
A large sum of the energy is not used directly for heating the food but dissipated during the process, hence higher energy bills.
|
| Induction Cooking | Electric Cooking | |
|---|---|---|
| (η) Effi ciency (η) | 80% | 65% |
| Temperature Control | Yes (Average Power Requirements 70%) |
No |
| (Pin) Power Input (Pin) | Pout/ η | Pout/ η |
| (Pin) Power output (Pin) | Pout * 1.25 | Pout * 2 |
| For the same Power Output | ||
| Power Input | 1.25 * (Power Output * 0.7) (w/ TemperatureControl) |
2.0 * Power output (w/o Temperature control) |
| Energy requirements | 1 : 2.3 | |
| Energy Savings | Save 56% (2.3-1) / 2.3 |